
1. High-Seas Mission Exposes Alarming Illegal Fishing in North Pacific
North Pacific – A recent high-seas surveillance operation uncovered widespread illegal activities in the North Pacific, including shark finning and the presence of “dark vessels” — ships operating without active tracking systems. The mission, involving multiple nations and coordinated through the North Pacific Fisheries Commission, identified numerous violations of international fishing regulations.
Shark finning, banned in many parts of the world, continues to be a major issue, with several vessels caught in the act. Detecting dark vessels highlights ongoing challenges in monitoring illegal fishing activities, as these unregistered ships often evade enforcement by turning off their tracking devices. The findings have sparked calls for stronger international cooperation and stricter penalties to protect vulnerable shark populations and ensure sustainable fishing practices.

2. Wildlife: Ecosystems: The Unexpected Heroes for Biological Diversity COP16
Cali, Colombia – At the ongoing COP16 of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), discussions spotlight the critical role of wildlife conservation in climate mitigation strategies. Wildlife and their habitats, including mangroves, forests, and wetlands, are seen as essential for carbon sequestration and ecosystem resilience. The conference emphasizes the integration of biodiversity protection with climate action, advocating for measures that safeguard species while combating climate change.
Delegates stressed the importance of addressing wildlife trafficking, habitat destruction, and unsustainable land use, which undermine conservation and climate goals. The CBD’s post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework aims to reinforce this integrated approach, urging nations to commit to protecting biodiversity as a climate solution.
Thank you for your generous gift that will help us continue the production of this weekly, free publication

3. New U.S. Rules Could Save Whitetip Sharks from the Brink of Extinction
The U.S. government is evaluating new regulations to protect oceanic whitetip sharks, a species currently facing severe population declines due to overfishing and bycatch. Once abundant in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, these sharks are now classified as “critically endangered.” The proposed rules include stricter bycatch limits and enhanced monitoring of fishing activities.
Conservation groups argue that immediate action is necessary to prevent the species from disappearing entirely, highlighting the sharks’ vital role in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems. These measures would bolster international efforts to curb illegal fishing practices and promote sustainable seafood industries if implemented.

4. In Colombia, Leaders Demand Less Talk, More Ocean Protection
Bogota, Colombia – In a new op-ed, former Colombian President César Gaviria and philanthropist Patti Harris argue that global commitments to ocean conservation are not translating into meaningful protections for marine life. Despite ambitious pledges, including the “30×30” target to protect 30% of the world’s oceans by 2030, enforcement remains weak, and marine ecosystems continue to degrade.
The authors call for stronger, legally binding agreements and increased marine protected areas (MPAs) funding. They emphasize that critical marine species and habitats could face irreversible damage without decisive action, undermining efforts to combat climate change and preserve biodiversity.

5. France Approves Bill to Ratify High Seas Treaty (BBNJ)
The French Parliament has approved a significant new bill to safeguard marine biodiversity. The legislation sets ambitious targets to expand marine protected areas (MPAs), strengthen enforcement against illegal fishing, and support habitat restoration projects. The bill aligns with France’s commitments under the UN’s Global Ocean Treaty, which seeks to protect 30% of the world’s oceans by 2030.
Environmentalists have praised the move as a vital step in reversing the decline of marine species, many of which are threatened by overfishing, climate change, and pollution. French officials believe the law will serve as a model for other nations, emphasizing that marine conservation is critical to sustaining the health of the global ocean ecosystem.

6. Saving the Ocean Is Key to Meeting Global Biodiversity Targets – Insights from Ocean Day
Cali, Colombia – Ocean Day at the ongoing Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) meeting underscored the interconnectedness of marine conservation and broader biodiversity goals. Experts highlighted the critical role of ocean ecosystems in achieving the framework’s targets, including protecting 30% of the world’s land and sea by 2030.
Discussions centered on enhancing marine protected areas (MPAs), combating illegal fishing, and addressing plastic pollution. Delegates called for stronger collaboration among nations to implement effective conservation measures and ensure sustainable use of marine resources. The event underscored the urgency of protecting ocean biodiversity as an integral part of global environmental strategies.
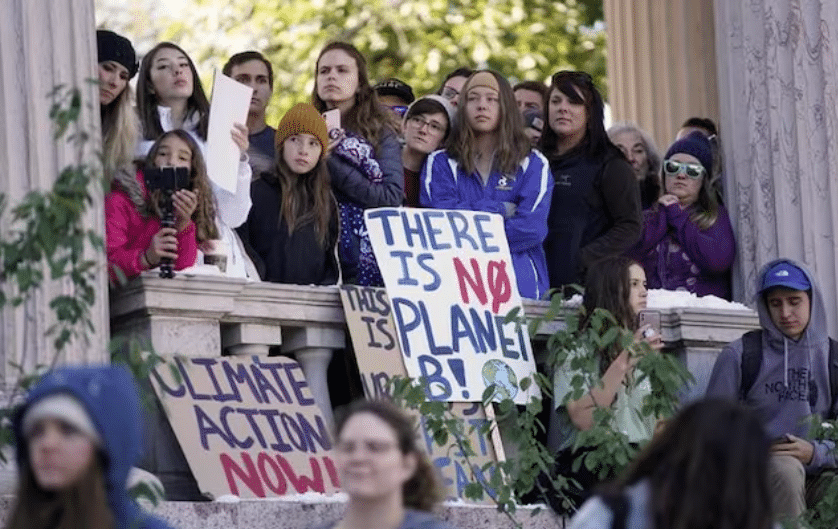
7. U.S. Supreme Court Rejects Youth Climate Case
Washington, D.C., USA – The U.S. Supreme Court declined to revive a high-profile climate lawsuit filed by young activists against the federal government. The plaintiffs argued that the government’s actions and inactions have exacerbated climate change, violating their constitutional rights to a healthy environment.
The case, initially filed in 2015, faced multiple legal setbacks, with courts ruling that such climate policy issues are better addressed by the legislative and executive branches rather than the judiciary. Advocates view the dismissal as a significant setback for youth climate movements, which have pushed for stronger environmental protections and action on climate change. Despite the ruling, the plaintiffs remain committed to pursuing other legal avenues and advocating for climate justice.

8. Fiji’s Climate Crisis: How Rising Seas Are Forcing Entire Communities to Relocate
Suva, Fiji – As a low-lying Pacific Island nation, Fiji is experiencing severe impacts of climate change firsthand, from rising sea levels to stronger cyclones. The government has initiated climate adaptation strategies, including relocating entire communities away from eroding coastlines. Fiji’s Prime Minister has called for urgent international action, highlighting the disproportionate impact on small island states that contribute minimally to global emissions.
Despite efforts, the nation struggles with the economic and social challenges of adapting to a rapidly changing environment. The situation in Fiji underscores the urgency of global cooperation to address climate change, particularly in vulnerable regions.

9. Groundbreaking DNA Research Exposes Hidden Threats to Endangered Sharks Worldwide
Miami, Florida, USA – Researchers at Florida International University have used advanced DNA techniques to reveal previously unknown risks to shark populations worldwide. By analyzing environmental DNA (eDNA) from water samples, scientists identified hidden threats such as illegal fishing and unreported bycatch, particularly affecting endangered species.
The study highlights the critical role of eDNA in monitoring marine biodiversity and informing conservation efforts. Many shark populations are already vulnerable due to overfishing, habitat loss, and climate change. The findings underscore the need for stricter enforcement of international fishing regulations and increased global collaboration to protect these apex predators from further decline.
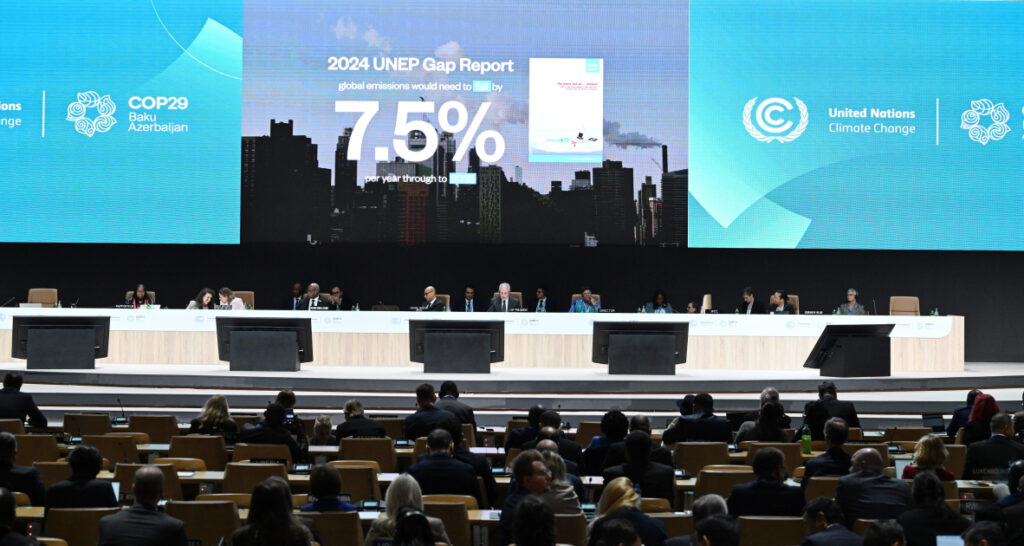

10. UN Climate Panel Calls for Urgent Action on Global Warming Goals
Dubai, UAE – IPCC Chair Jim Skea delivered a compelling address ahead of the COP29 climate conference, urging world leaders to accelerate climate action to meet the Paris Agreement targets. Skea emphasized the critical window of opportunity to limit global warming to 1.5°C, warning that current efforts are insufficient.
He highlighted the IPCC’s latest findings, indicating a sharp rise in climate-related disasters, and underscored the need for mitigation and adaptation strategies. Skea called for immediate investments in renewable energy, stronger emissions reductions, and enhanced climate resilience measures to protect vulnerable communities and ecosystems.

11. Climate Policy Clash: Starmer vs. Trump Sparks U.K. Debate
London, England – The climate policy debate in the U.K. has intensified with recent comments from political figures, including Labour leader Keir Starmer and former U.S. President Donald Trump. Starmer reiterated his commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, while Trump criticized such goals as economically damaging.
The diverging perspectives reflect broader global divisions on climate action, with advocates pushing for stronger measures amid escalating climate impacts and critics expressing concerns over the economic implications. Analysts note that these debates will likely influence upcoming elections and the U.K.’s climate strategy moving forward.
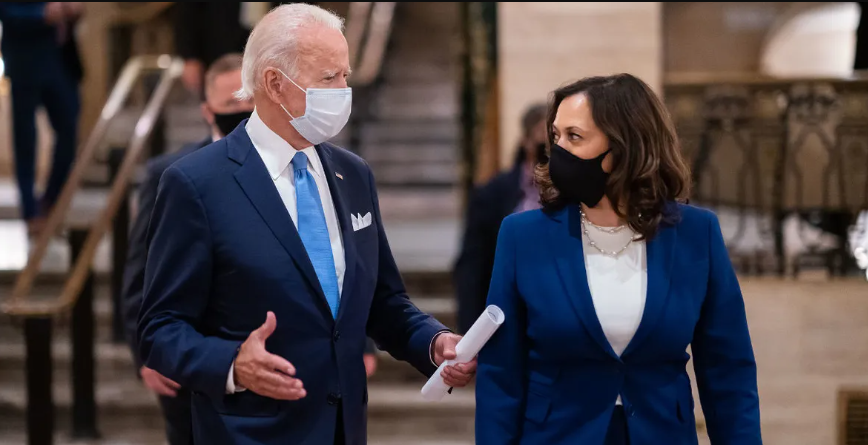

12. Biden-Harris Team Urges Stronger Climate Action at COP29
Washington, D.C., USA – In a comprehensive fact sheet, the Biden-Harris Administration emphasized its commitment to leveraging U.S. climate leadership at COP29. The administration urges global partners to accelerate efforts to reduce emissions, invest in renewable energy, and enhance climate resilience.
Key initiatives highlighted include the Inflation Reduction Act, aimed at cutting U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by 40% by 2030 and increased international climate finance to support developing countries. The fact sheet outlines specific domestic actions, such as expanding clean energy infrastructure, and calls for greater ambition from other nations to meet Paris Agreement targets. This announcement underscores the administration’s strategy to solidify the U.S. role in driving global climate action.
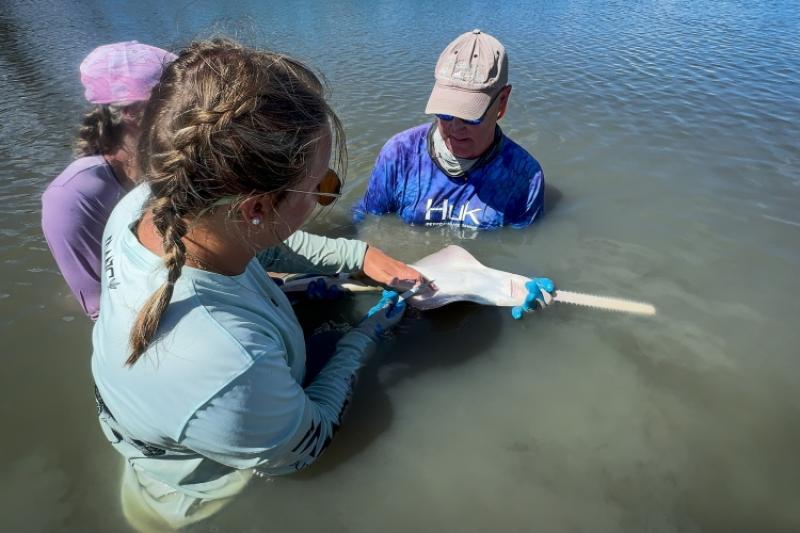

13. NOAA’s 15-Year Mission to Track Endangered Smalltooth Sawfish
Miami, Florida, USA – NOAA scientists have spent 15 years studying the elusive smalltooth sawfish, a critically endangered species found off the southeastern coast of the U.S. Using satellite tags and field surveys, the team has gathered valuable data on the sawfish’s movements, habitat preferences, and population trends.
Despite conservation measures, the species faces ongoing threats from habitat destruction, entanglement in fishing gear, and climate change. NOAA’s research aims to inform recovery strategies, enhance protections, and increase public awareness about this unique marine species. The sawfish, with its distinctive elongated snout, serves as a key indicator of ecosystem health.
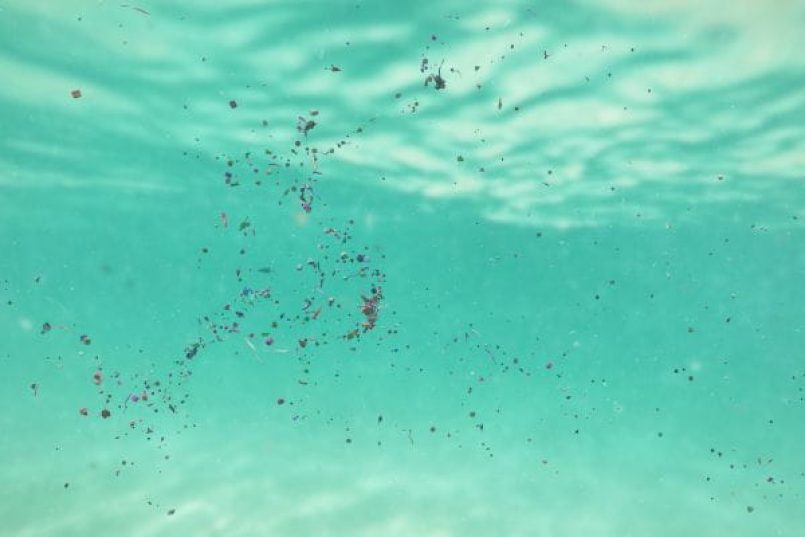

14. Study: Ship Coatings Contribute to Ocean Microplastic Pollution
This study highlights the significant contribution of microplastics to marine pollution from ship biofouling in-water cleaning. Key sources include the weathering and abrasion of marine coatings during ship maintenance. Marine coatings, rich in polymers like polyurethanes and epoxies, are released into the ocean through normal wear and tear, damage, in-water cleaning, and removal of old paint layers. The global shipping sector is identified as a substantial contributor, potentially releasing thousands of tons annually.
Predictive modeling identifies bulk carriers as the largest contributors, followed by tankers, containerships, and cargo vessels. Manual biofouling cleaning by divers generates more microplastics than mechanized in-water cleaning (IWC) systems with debris capture. Proposed mitigation strategies include alternative cleaning methods and improved waste capture and processing, though their effectiveness remains to be determined due to implementation challenges. A multidisciplinary approach and coordinated global efforts are essential to develop effective strategies for reducing microplastic pollution from ship coatings and protecting marine ecosystems.

15. Oceans Gain Momentum at COP16 Biodiversity Conference
Cali, Colombia – At the COP16 Biodiversity Conference, the health of the world’s oceans took center stage, with nations agreeing on ambitious targets to protect marine biodiversity. Discussions focused on expanding marine protected areas (MPAs), addressing illegal fishing, and mitigating the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems.
Experts highlighted the importance of safeguarding coastal habitats, like mangroves and coral reefs, which are vital carbon sinks. The conference marked a significant step forward in integrating ocean conservation into global biodiversity efforts.

16. Blue Carbon Boom: Investors Bet Big on Ocean Offsets
The marine carbon market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increased demand for carbon offsets tied to ocean-based projects. A new report indicates a surge in investments in blue carbon initiatives, such as seagrass restoration and mangrove conservation, known for their high carbon sequestration potential.
The market’s expansion is bolstered by corporations seeking to meet net-zero commitments and capitalize on the growing recognition of blue carbon’s role in mitigating climate change. However, concerns remain about the lack of standardized verification methods and the risk of greenwashing. Industry experts are calling for stronger regulations to ensure the integrity of marine carbon offset projects.
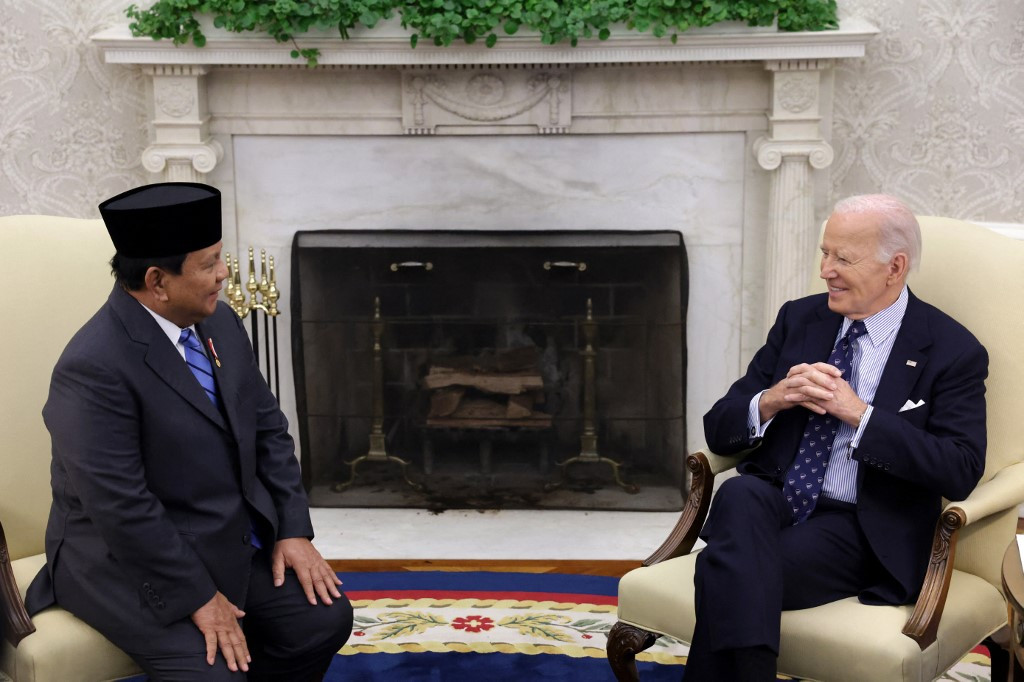

17. Biden and Subianto Strengthen U.S.-Indonesia Climate Alliance
Washington, D.C., USA – President Biden and President Prabowo Subianto commemorated 75 years of U.S.-Indonesia diplomatic relations, highlighting the countries’ growing partnership on climate, trade, and regional security. The leaders discussed initiatives to enhance renewable energy cooperation, focusing on investments in Indonesia’s transition to clean energy.
They pledged increased support for forest conservation, aiming to curb deforestation while promoting sustainable development. On security, both nations committed to strengthening maritime patrols in the Indo-Pacific, addressing shared concerns over illegal fishing and regional stability. The meeting underscored a mutual commitment to tackling global climate change and fostering economic resilience.

18. New Tool Highlights Climate Risks in Madagascar’s Coastal City
Toamasina, Madagascar – The Stimson Center has introduced the Climate and Ocean Risk Vulnerability Initiative (CORVI), a tool designed to assess climate risks in coastal cities, to the port city of Toamasina. CORVI analyzes factors such as rising sea levels, economic vulnerabilities, and ecosystem health to provide a comprehensive risk profile.
In Toamasina, the tool highlighted significant threats from coastal erosion, increased storm intensity, and economic dependence on fisheries. The findings will inform climate adaptation strategies, helping local governments prioritize resilience projects. The initiative underscores the urgent need for integrated climate risk assessment tools to support decision-making in vulnerable coastal regions.

19. Endangered Birds Return to Kamaka Island After 100 Years
Kamaka Island, French Polynesia – Endangered bird species have successfully nested on Kamaka Island for the first time in over a century, marking a significant victory for conservationists. The return of the birds, including the critically endangered Polynesian Storm-Petrel, follows a decade-long effort by Island Conservation and local partners to eradicate invasive predators.
The restoration of Kamaka’s native habitats has allowed these rare birds to breed safely, offering hope for their recovery. This achievement highlights the importance of invasive species management in protecting vulnerable island ecosystems and restoring biodiversity.
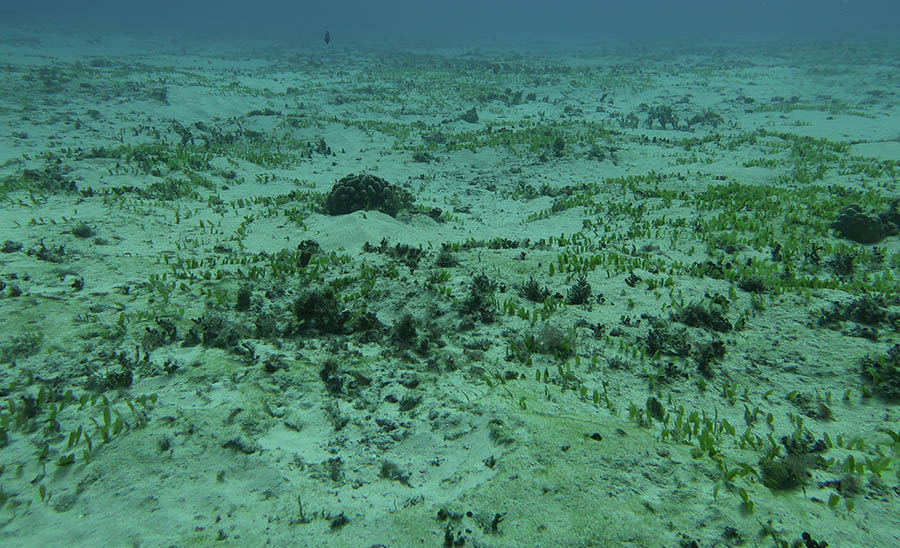

20. Maunalua Bay Launches Comprehensive Marine Monitoring Initiative
Maunalua Bay, Hawaii, USA – Hawaii’s Division of Aquatic Resources (DAR) manages, conserves, and restores the state’s unique aquatic resources and ecosystems. One of their key initiatives is the Fish and Habitat Utilization (FAHU) surveys. These surveys are designed to monitor marine ecosystems and inform management decisions. This month, the Oʻahu DAR monitoring team began implementing FAHU surveys in Maunalua Bay.
These surveys consist of a 25-meter belt fish transect paired with benthic images at every meter mark. The benthic images are later used to evaluate the composition of the benthic community. This method helps establish a baseline for the proposed fishery management area in Maunalua Bay and allows for statewide comparisons of Hawaii’s marine ecosystems.
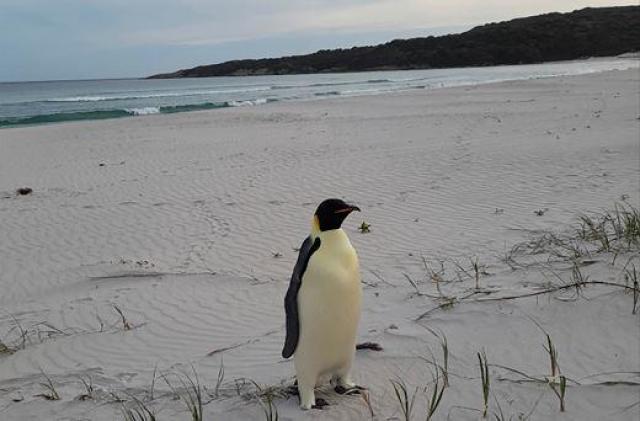

21. Malnourished Emperor Penguin Washes Ashore in Australia, 2,000 Miles from Home
Melbourne, Australia —An emperor penguin was found malnourished on a beach in Denmark, Australia, far from its Antarctic home. This is the first time an emperor penguin has been reported in Australia, though some have reached New Zealand. The penguin, named Gus, was discovered by a local surfer and is now being cared for by a wildlife expert.
Gus is being sprayed with chilled water to help him cope with the warmer climate. Climate change directly threatens Emperor penguins, as their survival and breeding are tied to sea ice, which is disappearing due to rising temperatures. The Western Australia Biodiversity Department is focused on rehabilitating Gus, with options for his return to Antarctica still being considered.

22. Indonesia Launches New Model for Protected Area Conservation
Jakarta, Indonesia – The Indonesian government unveiled a new model to maximize the potential of its conservation areas, which cover nearly 27% of the nation’s territory. The plan focuses on integrating community participation, enhancing biodiversity protection, and developing eco-tourism.
Officials highlighted that conservation efforts often lack the financial support and comprehensive management needed for long-term sustainability. The new strategy bridges these gaps by attracting investment and fostering partnerships with local stakeholders. If successful, the model could serve as a blueprint for other Southeast Asian nations looking to strengthen their conservation initiatives.

23. East Asia Local Governments Unveil Bold Coastal Management Strategies
Xiamen, China –The PEMSEA Network of Local Governments (PNLG) Annual Forum, held during the 2024 East Asian Seas Congress and World Ocean Week in Xiamen, focused on sustainable coastal and marine management. Approximately 100 participants attended the event, including representatives from 21 PNLG regular members, five associate members, and marine experts from various countries. The forum featured discussions on marine ecosystem restoration, climate resilience, and coastal ecosystem protection.
Keynote speeches highlighted China’s beach nourishment practices and Xiamen’s integrated coastal management model. The PNLG General Assembly saw the signing of cooperation agreements and the introduction of new members. Field trips showcased Xiamen’s smart port and ecological restoration efforts. The forum emphasized knowledge sharing, joint planning, and future cooperation to enhance marine and coastal governance in the East Asian Seas region.

24. Marine Conservation Workshop Highlights Challenges for Caribbean Fisheries
Calliaqua, St. Vincent and the Grenadines – Fishery stakeholders from across the Caribbean gathered in Calliaqua for a workshop focused on enhancing marine conservation efforts. Discussions centered on the growing threats of overfishing, climate change, and habitat degradation.
Participants emphasized the need for stronger enforcement of existing regulations and better data collection to support sustainable fisheries management. The workshop also highlighted successful community-led initiatives that are helping to rebuild fish stocks. Organizers called for increased regional cooperation and capacity-building to protect the Caribbean’s vital marine ecosystems and the livelihoods they support.

25. ASEAN, East Asia Renew Partnership for Resilient Seas at Congress
Xiamen, China – The ASEAN Centre for Biodiversity (ACB) and the Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia Resource Facility (PRF) renewed their partnership at the East Asian Seas Congress 2024 in Xiamen, China. This collaboration, through the ASEAN ENMAPS project, aims to enhance marine conservation across Southeast Asia.
The project focuses on managing marine protected areas and improving coastal and marine management systems. Funded by the Global Environment Facility and implemented by the United Nations Development Programme, ASEAN ENMAPS targets four large marine ecosystems with pilot sites in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand. The renewed partnership emphasizes strengthening policies, capacity development, and knowledge-sharing to support sustainable regional marine governance and resilience.
26. Will COP29 Be the Turning Point for Global Climate Action? New Report Raises Tough Questions
As the world prepares for COP29, a new analysis by Bloomberg examines whether current climate pledges are enough to meet the 1.5°C target set by the Paris Agreement. The report highlights that while progress has been made, most countries still fall short of their commitments. Key issues include insufficient financing for climate adaptation, slow transitions to renewable energy, and rising greenhouse gas emissions from major economies.
The upcoming summit is expected to focus on scaling up ambition, with calls for more aggressive emission reduction targets and stronger enforcement mechanisms.
