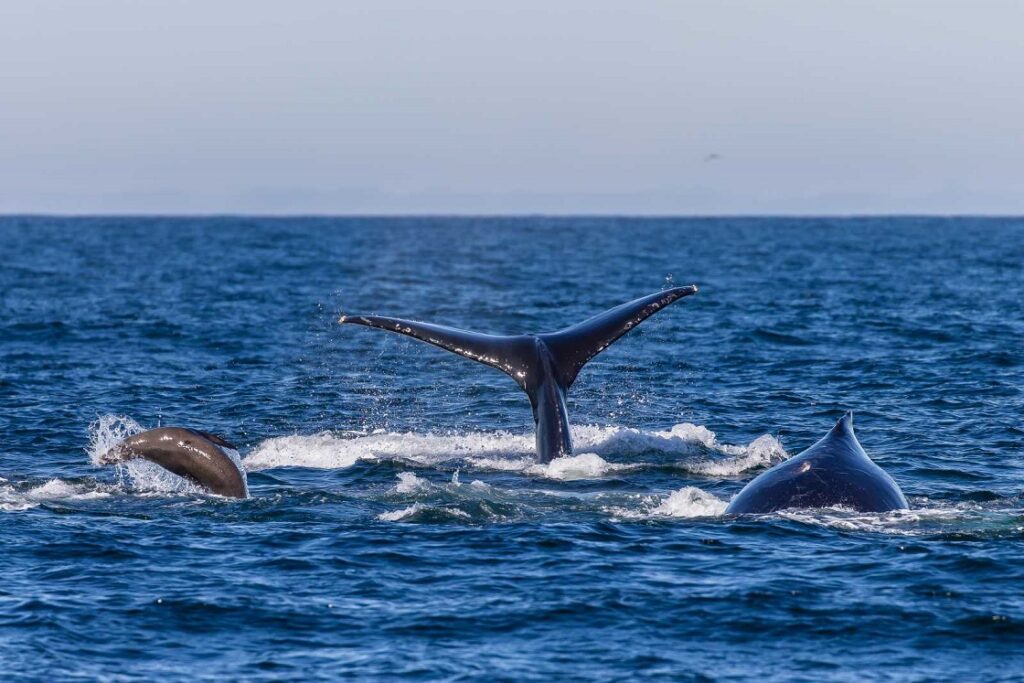

1. Marine Mammals Bounce Back: But Will Conservation Efforts Be Enough?
Conservation teams are celebrating the resurgence of marine mammal populations after decades of protection. However, scientists warn that climate change and pollution remain significant threats.
A recent study outlines the success stories, like gray whales, while urging a continued focus on habitat restoration and stricter regulations. The research advocates for strengthening conservation policies to secure these gains.
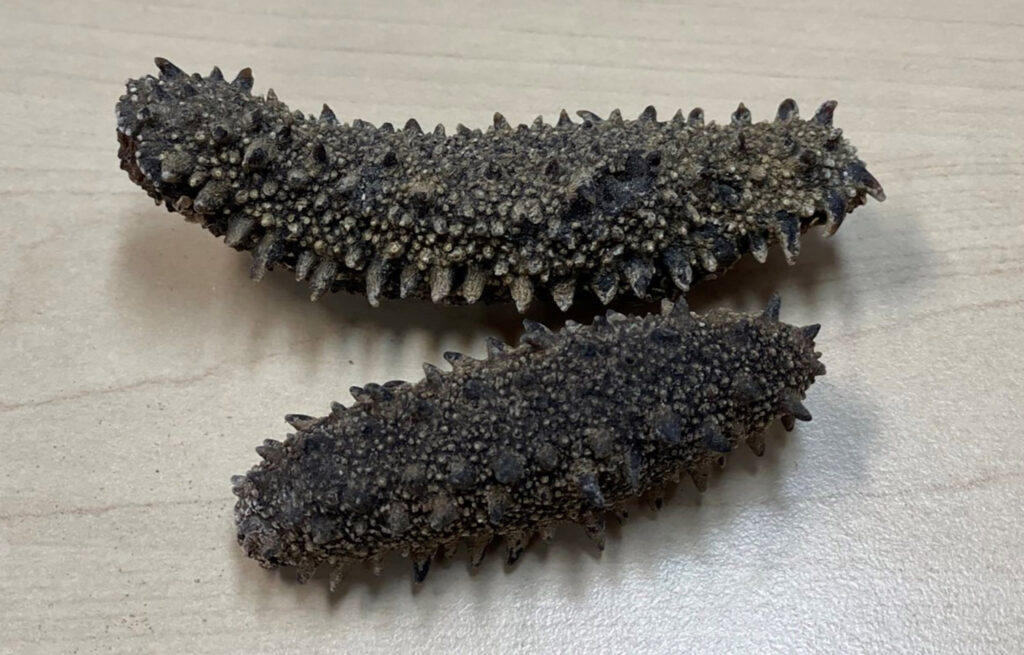

2. China Wields Influence at FAO to Shape Endangered Species Policies
In Rome, Italy, China is leveraging its position within the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) to influence global conservation decisions, particularly those made by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES). A recent academic paper reveals that China employs ‘venue linking’ strategies, using its clout in one international body to sway outcomes in another.
This approach has been evident in cases like the prevention of the Apostichopus japonicus sea cucumber from being listed as endangered, a move that aligns with China’s commercial interests in sea cucumber production. Such actions underscore the complex interplay between national economic goals and international conservation efforts, raising questions about the impartiality of global environmental governance.
Thank you for your generous gift that will help us continue the production of this weekly, free publication
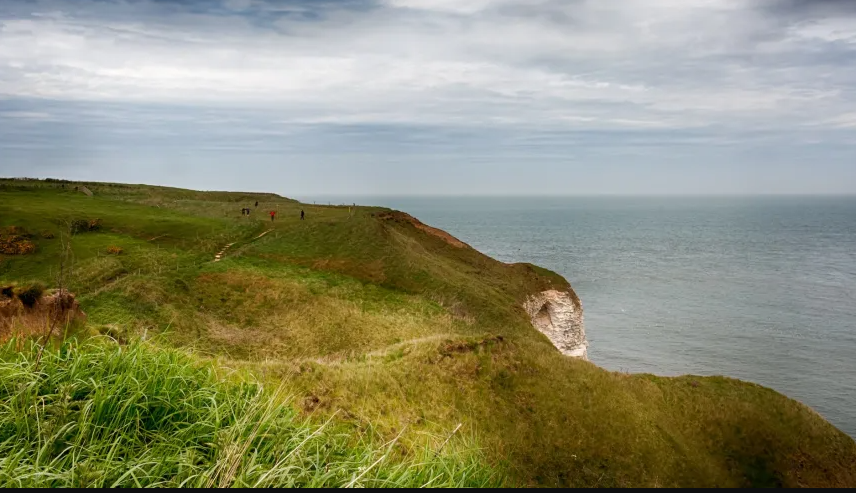

3. Experts Surprised at Positive Discoveries off the Coast of England
In London, United Kingdom, the North Sea’s marine life is experiencing a remarkable resurgence after decades of decline due to overfishing and oil exploration. Between the 1950s and 1980s, these activities led to a 97% loss of biomass. However, recent conservation efforts, including bans on sandeel fishing and reduced oil production, have facilitated the return of bottlenose dolphins, grey seals, and minke whales.
Tony Juniper, chair of Natural England, emphasized nature’s resilience, stating, “The wonderful thing about nature is that it can recover pretty quickly if you give it the chance.” Despite these positive trends, challenges persist, such as opposition from the European Union regarding the UK’s sandeel fishing ban. Continued international cooperation and long-term conservation strategies are essential to sustain and enhance this ecological recovery.

4. Strategic Planning Could Reduce Farm-Scale Mariculture Impacts on Marine Biodiversity
Researchers have conducted a comprehensive assessment of mariculture’s effects on 20,013 marine species across ten taxonomic groups. Their findings suggest that strategic planning in mariculture operations can significantly mitigate negative impacts on marine biodiversity. By carefully selecting farm locations and implementing sustainable practices, the aquaculture industry can coexist more harmoniously with marine ecosystems.
This approach not only preserves biodiversity but also promotes the long-term viability of mariculture as a food source. The study emphasizes the importance of integrating ecological considerations into the expansion plans of mariculture to ensure minimal disruption to existing marine life. Such proactive measures are crucial for balancing the growing demand for seafood with the need to protect our oceans’ health.
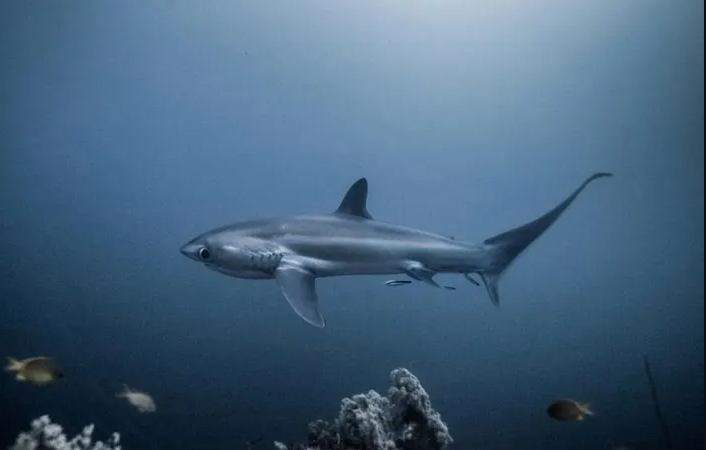

5. Alternative Livelihoods in Indonesia Offer Hope for Endangered Thresher Sharks
In Jakarta, Indonesia, innovative strategies are being implemented to protect the pelagic thresher shark populations. By diversifying local incomes, communities are reducing their reliance on shark fishing, which has historically threatened these majestic creatures. Initiatives include promoting ecotourism and sustainable fishing practices, providing alternative revenue streams for local fishermen.
These efforts not only safeguard the thresher sharks but also enhance the economic resilience of coastal communities. The success of these programs highlights the potential of community-driven conservation models in addressing environmental challenges. As more locals engage in shark conservation, there’s renewed hope for the future of these species and the ecosystems they inhabit.
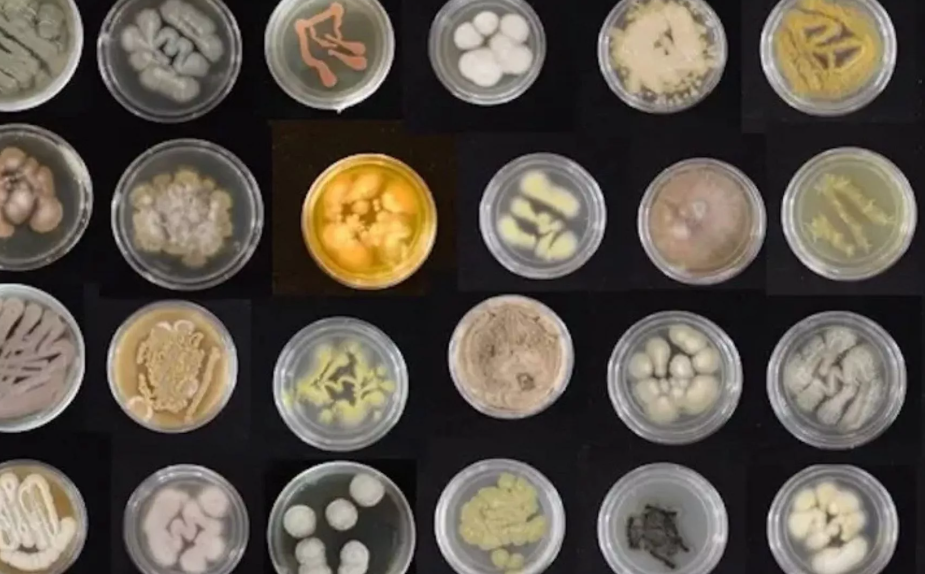
6. Hawaiian Scientists Train Marine Fungi to Devour Ocean Plastics
In Honolulu, Hawaii, researchers are pioneering a novel approach to combat ocean pollution by training marine fungi to consume plastics. These ‘hungry’ fungi have demonstrated the ability to break down polyurethane, a prevalent plastic, at an accelerated rate. By harnessing the natural appetites of these microorganisms, scientists aim to reduce the vast amounts of plastic waste accumulating in marine environments.
This innovative method offers a sustainable solution to the global plastic crisis, potentially transforming waste management practices. While challenges remain in scaling this technology, the research signifies a promising step toward cleaner oceans and a healthier planet.
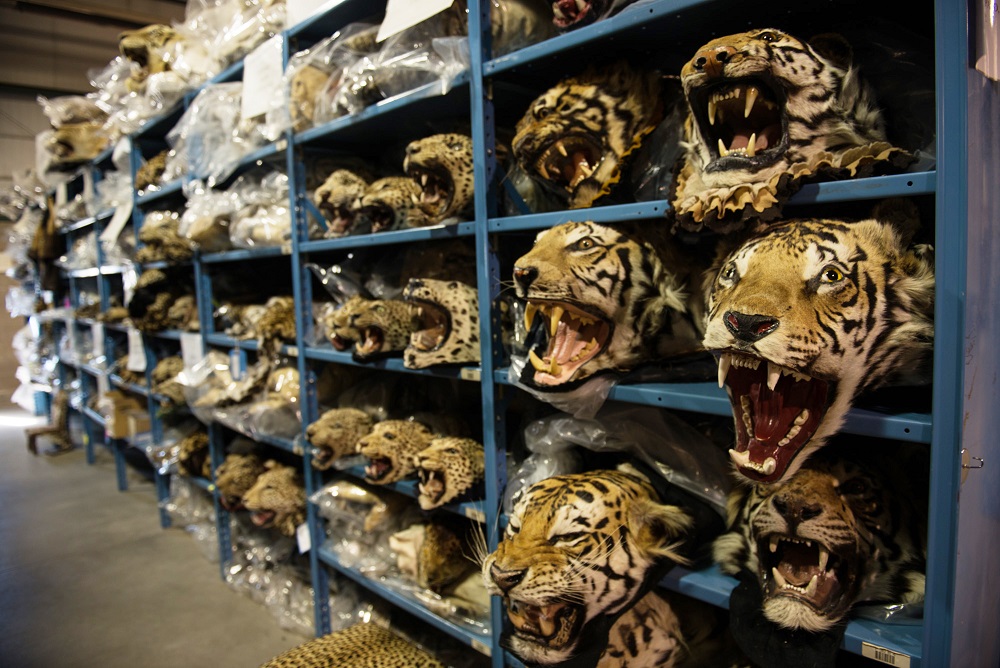

7. U.S. Demand for Exotic Pets Fuels Global Wildlife Trade
In Washington, D.C., United States, the nation’s insatiable appetite for exotic pets is intensifying the global wildlife trade, raising significant environmental and ethical concerns. From reptiles to rare birds, the U.S. stands as a major consumer, often sourcing animals through illicit channels that threaten species survival and biodiversity. This demand not only endangers the captured wildlife but also disrupts entire ecosystems and contributes to the spread of zoonotic diseases.
Conservationists urge stricter regulations and increased public awareness to curb the import of exotic species. By addressing consumer behavior and enforcing robust legal frameworks, the U.S. can play a pivotal role in mitigating the adverse impacts of the global wildlife trade and promoting the preservation of endangered species worldwide.

8. California Enacts Emergency Measures to Protect Shrimp and Crab Fisheries
In Sacramento, California, the Fish and Game Commission has implemented emergency regulations targeting the commercial coonstripe shrimp fishery to mitigate whale entanglement risks. The new rules establish a management boundary at the Sonoma-Mendocino County line, impose a 30-fathom depth limit for northern fisheries, and restrict the number of traps and vertical lines per vessel.
Additionally, the Commission approved an experimental fishing permit to test longlining gear in the Dungeness crab fishery. This method connects multiple traps via a groundline retrieved by a grapple, eliminating vertical lines that pose entanglement hazards. These proactive measures aim to balance commercial fishing interests with the imperative of marine wildlife conservation, ensuring the sustainability of California’s vital seafood industries.

9. Ambitious ‘Dos Mares’ Project Aims to Create Vast Marine Reserve in Baja California Sur
In La Paz, Mexico, a coalition of environmental organizations and local fishermen is advocating for the establishment of the Dos Mares (Two Seas) Biosphere Reserve off the coast of Baja California Sur. The proposed marine protected area would encompass approximately 192,000 square kilometers, extending 50 miles offshore into both the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of California.
Supporters argue that the reserve would help Mexico fulfill international conservation commitments while bolstering local economies through sustainable fishing and increased tourism. However, some coastal fishing communities express concerns about potential restrictions on traditional practices. Balancing ecological preservation with the livelihoods of local populations remains a central challenge as the project moves forward.
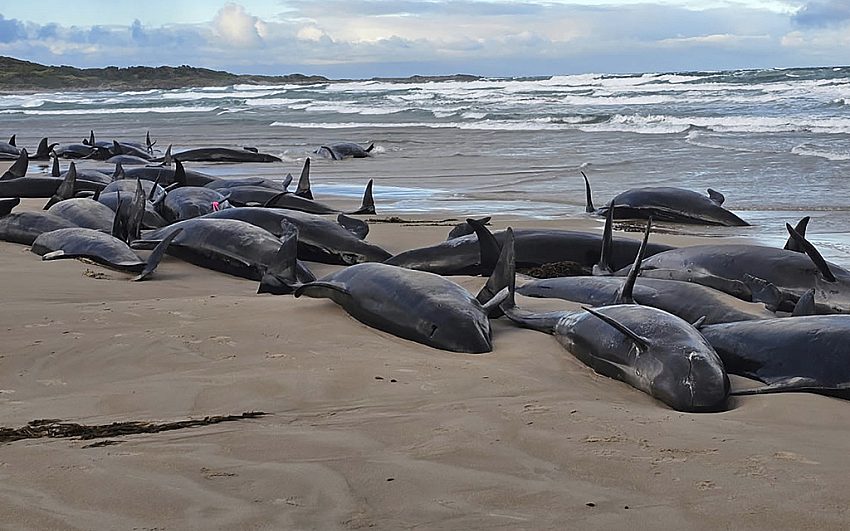

10. Tragic Mass Stranding: 90 Whales to Be Euthanized on Tasmanian Beach
In Hobart, Australia, a devastating event unfolded as 157 false killer whales stranded themselves on a remote Tasmanian beach. Discovered by a local resident, only 90 of these marine mammals were still alive upon the arrival of experts. Despite concerted rescue efforts by marine biologists and veterinarians, unfavorable ocean and weather conditions thwarted attempts to refloat the whales, leading to the heart-wrenching decision to euthanize them to prevent further suffering.
False killer whales, a type of dolphin resembling orcas, are protected under Australian law. This incident marks the first mass stranding of false killer whales in Tasmania since 1974. The exact cause of the stranding remains unknown, though highly social species like these are more susceptible to such events. Authorities have closed part of the beach to the public during this distressing time.
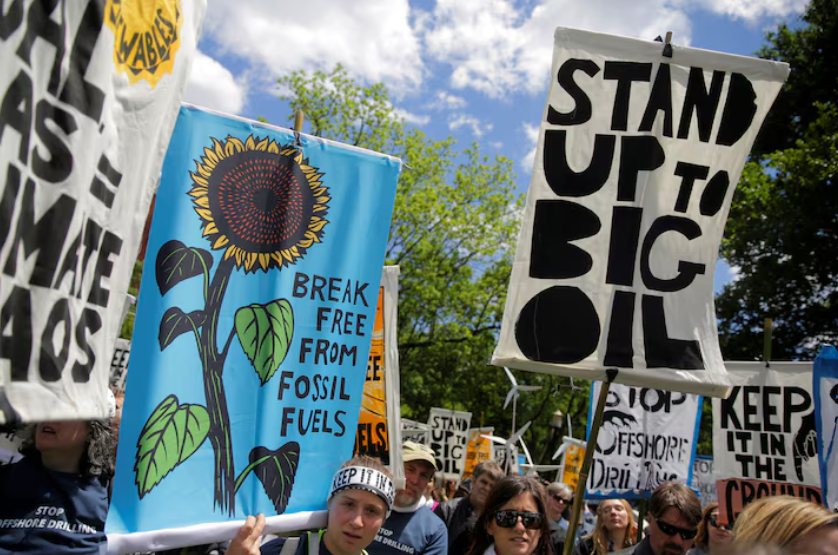

11. Environmental Groups Sue to Block Trump’s Offshore Drilling Expansions
In Washington, D.C., United States, environmental organizations have filed a lawsuit against the Trump administration’s recent decision to revoke former President Joe Biden’s ban on offshore drilling in certain coastal areas. The legal action seeks to reinstate protections for approximately 128 million acres in the Arctic and Atlantic oceans.
The plaintiffs argue that the administration lacks the authority to reverse the previous prohibitions and express concerns over potential environmental risks associated with expanded offshore drilling. The administration contends that increasing offshore energy production is vital for economic growth and energy independence. This lawsuit represents a significant legal challenge to the administration’s energy policies concerning offshore resource development.
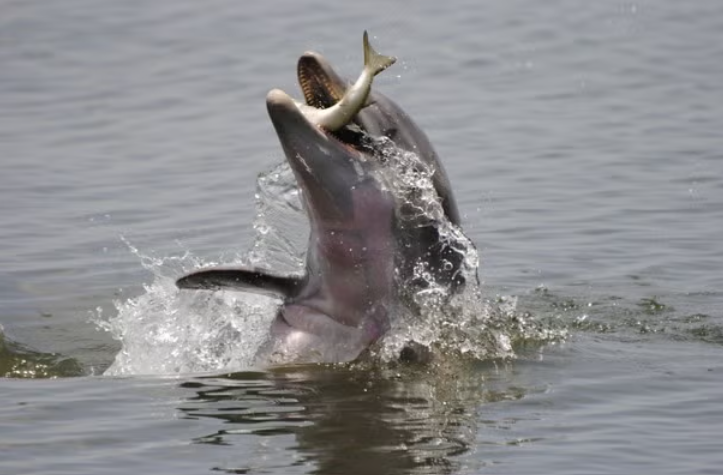

12. Florida’s Dolphin Deaths Linked to Ecological Crisis in Indian River Lagoon
Florida, USA, Research indicates that unusual dolphin mortalities in the Indian River Lagoon are due to shifts in ecosystem health. Decreased fish stocks and changes in prey availability are forcing bottlenose dolphins to adapt their diets, leading to increased stress and mortality.
The findings underscore the growing impacts of climate change and human activities, stressing the urgency for effective conservation measures to protect marine species and their habitats.
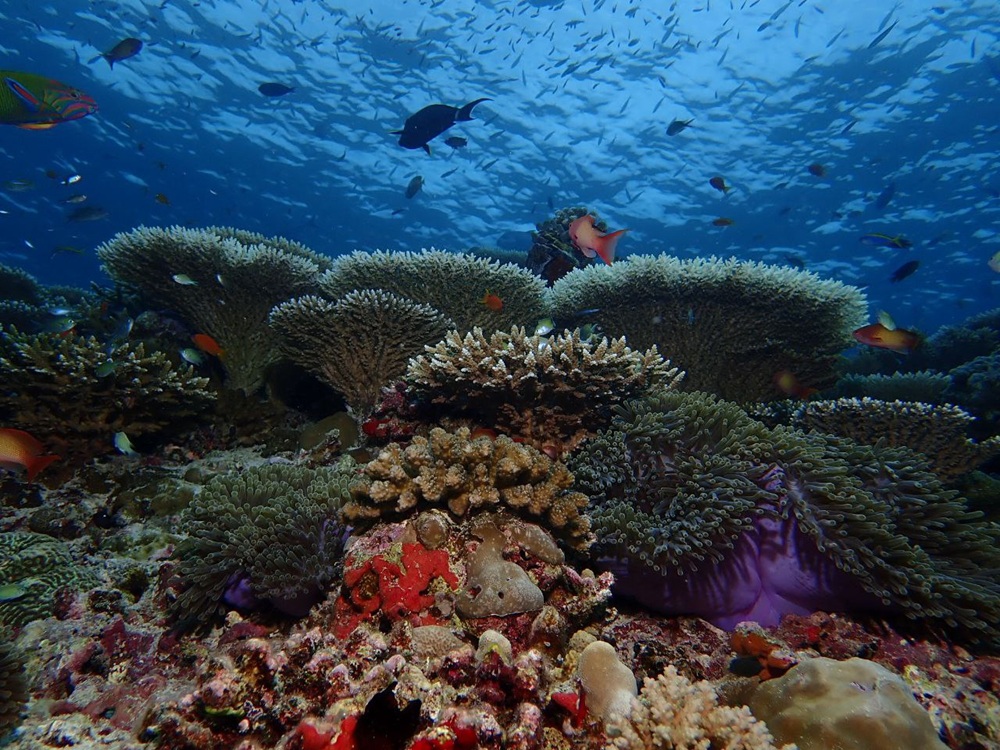

13. Zanzibar’s Bawe Island Declares New Marine Reserve to Protect Coral Reefs
In Zanzibar City, Tanzania, Bawe Island has announced the establishment of the Changuu-Bawe Marine Conservation Area in collaboration with the Zanzibar government. This initiative aims to safeguard the island’s vibrant coral reefs and diverse fish populations, ensuring the preservation of its rich marine biodiversity for future generations.
The reserve not only focuses on environmental conservation but also supports local fishing communities by promoting sustainable practices. This development underscores the region’s commitment to balancing ecological preservation with community livelihoods.
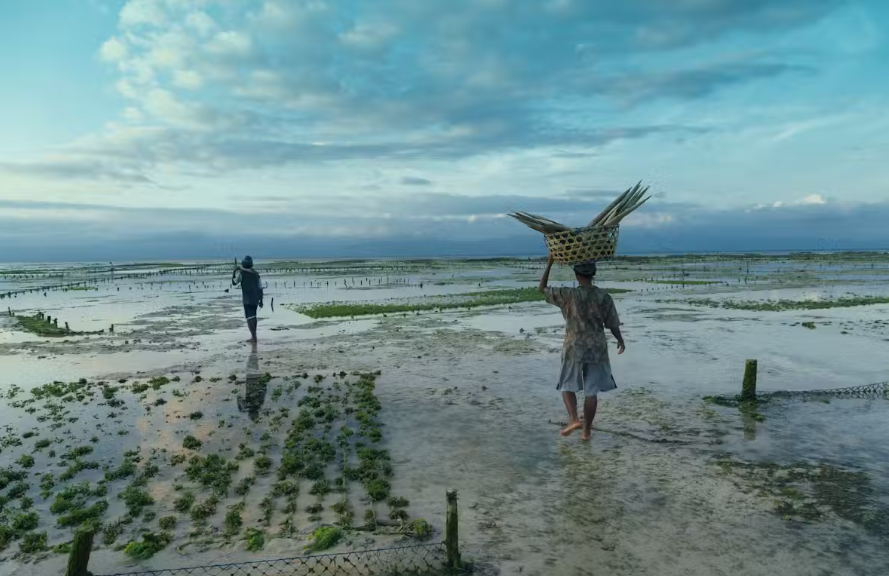

14. Expanding Seaweed Farms Threaten Essential Marine Habitats
Scientists are raising concerns about the rapid expansion of seaweed farming and its potential risks to vital marine ecosystems. While seaweed cultivation offers benefits such as carbon sequestration and alternative livelihoods, unchecked growth may disrupt coastal habitats, affecting species that rely on these environments.
Researchers advocate for comprehensive environmental assessments and the implementation of sustainable farming practices to mitigate adverse impacts. Balancing industry growth with ecological preservation is crucial to maintaining the health of marine biodiversity.

15. National Conference Addresses Challenges Facing Working Waterfronts
In San Diego, California, the seventh annual National Working Waterfront Network (NWWN) conference convened to discuss the pressing issues confronting America’s working waterfronts. Participants highlighted the importance of collaboration among commercial and recreational fisheries, ports, and waterfront businesses to tackle challenges such as climate change, fishery collapses, and the need for improved communication between scientists and industry stakeholders.
The conference emphasized partnerships with organizations like Sea Grant and NOAA Fisheries as essential for resilience and adaptation. Discussions also focused on mental health support for fishermen and community engagement through education and policy initiatives.

16. Revealing UK’s Hidden Oil Spills: The Unsettling Truth
London, United Kingdom – An alarming new map from Oceana UK exposes the vast scale of oil and chemical spills in UK waters, revealing over 82,000 kg of oil and 149,000 kg of chemicals dumped in 2024.
The report highlights gaps in spill reporting, with many incidents not publicly disclosed. Oceana urges for more transparency and a ban on new offshore drilling projects to protect marine life and sensitive ecosystems.
